Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

1. This week at Market Urbanism Shane Phillips points the finger to a major culprit in LA‘s affordability problems: Keep Los Angeles Affordable By Repealing Proposition U Of the 29,000 acres zoned for commercial and industrial uses throughout LA, 70 percent saw their development capacity sliced in half, from a floor-area ratio (FAR) of 3.0 to 1.5. Since the city allows housing to be built in many of these zones, it didn’t just mean less office, retail, and manufacturing space, but fewer homes as well. Emily Washington contributed to New Urbs at The American Conservative: Family-Friendly Cities Start With Schools But where I depart from Schwarz is that public policy, not economic forces or renter preferences, is largely responsible for the lack of children in American cities. Specifically, education policy. 2. Where’s Scott? Scott Beyer took a writing break this week to wander around Texas, visiting the towns of Cuero, Victoria, Corpus Christi, Kingsville, Brownsville, McAllen, and the Mexican border city of Reynosa. He has since returned to Dallas, and will be flying this week to Boulder, CO, for the first annual YIMBY conference. Tickets for the event are still available. 3. At the Market Urbanism Facebook Group Alden Wilner creates a Wikipedia stub for Market Urbanism, Russ Nelson adds to it. We’d love to see the hive mind expand the page! Adam Millsap‘s latest: What The Boom And Bust Of Williston, ND Teaches Us About The Future Of Cities via Jonathan Coppage at New Urbs: Rescue Cities for Families Shanu Athiparambath wrote, Indian Cities Need Private Fire Stations Matt Robare sums up the Massachusetts zoning reform, which passed the Senate Alex Bernstein wants to know the best objective and unbiases books to start reading Asher Meyers suggest the benefit of Universal Basic Income extends to urban issues based on Charles Murray‘s editorial […]
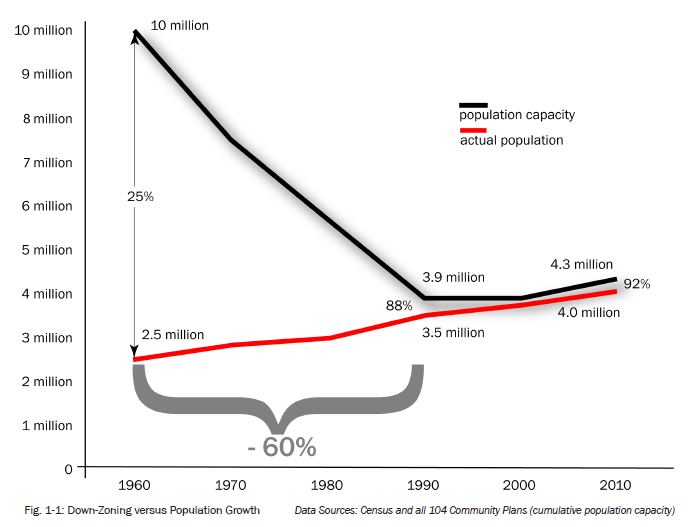
In 1986, a foreshadowing of today’s fight over “neighborhood integrity” was taking place, culminating in November as Los Angeles residents voted 2-to-1 to cut the development potential of thousands of parcels across the city. Of the 29,000 acres zoned for commercial and industrial uses throughout LA, 70 percent saw their development capacity sliced in half, from a floor-area ratio (FAR) of 3.0 to 1.5. Since the city allows housing to be built in many of these zones, it didn’t just mean less office, retail, and manufacturing space, but fewer homes as well. The ballot initiative responsible for these changes was called Proposition U, and it’s the reason that so many commercial corridors in LA are still characterized by 1960s and ’70s-era, single-story, dilapidated strip malls. All those arterial corridors were the ones permanently frozen in time by Prop U. THE PROPOSAL To my knowledge no one has ever assessed exactly how much this instance of “planning by the ballot” actually reduced the residential capacity of Los Angeles. By my very, very rough estimate, I would put the number somewhere on the order of 1 million homes.* But whether the actual number is 1 million, 500K, or over 2 million, the conclusion is the same: If we want to keep Los Angeles affordable for residents at all income levels, we should repeal Proposition U. Repealing Proposition U would achieve several important aims. Since we’re talking about arterial, commercial corridors, the repeal would dramatically increase the supply of transit-oriented housing over the next several decades—something we desperately need at a time of record-low residential vacancy rates if we’re to have any hope of limiting continued rent increases. It would reduce development pressures on existing communities, directing development to underutilized corridors with little to no housing on them, rather than funneling developers into single-family neighborhoods […]
1. This week at Market Urbanism Michael Lewyn dispels some common misconceptions about Jane Jacobs And High-Rises So I’m not sure she would have favored the common modern idea that high-rise and low-rise buildings should be segregated from each other, or that buildings of different density are “out of scale.” Despite auto-centric regulation and subsidies, Houston‘s “zoning lite” approach seems to be working, according to Nolan Gray in Houston’s Beautiful (yet Partial) Embrace of Market Urbanism This fourth city has managed to balance a booming economy, explosive population growth, and affordable housing. This city has—as cities have for thousands of years—steadily grown denser, more walkable, and more attractive to low-income migrants seeking opportunity. This city is Houston, and it’s well past time for her to come out of the shadows. 2. At the Market Urbanism Facebook Group via Adam Hengels: a clip of a speech by Will Arnett’s character in Netfllix’s series “Flaked” who drops the Venice Beach NIMBYs and comes out as a YIMBY via Krishan Madan: “At a time of such high demand, higher density construction should be legalized” via Adam Hengels: Rethinking a Century of Zoning Andy Walker wants to know who’s going to be at CNU in Detroit this weekend via Krishan Madan: Van Bramer To Block Phipps’ 210-Unit [Affordable Housing] Development Plan, Essentially Kills Proposal (in Queens) Nick Zaiac shared an interesting table from NAHB, who found regulations to account for nearly 1/4 of the cost of new home prices Andrew Atkin shared his predictions of a “Utopian” sprawl, Urbanists cringe via Adam Millsap: Clean money, dirty system: Connected landowners capture beneficial land rezoning Nick Zaiac found some “Good stuff from the Richmond Fed on infrastructure, parking, and reform options” via Roger Valdez: HALA’S Most Confusing Recommendation: The Pushes and Pulls of MIZ (Seattle) via Roger Valdez: Seattle may slap new rules on Airbnb […]

A metropolitan economy, if it is working well, is constantly transforming many poor people into middle-class people, many illiterates into skilled people, many greenhorns into competent citizens. … Cities don’t lure the middle class. They create it. – Jane Jacobs, The Death and Life of Great American Cities If you follow urban issues in the press, you might be forgiven for thinking that there are only three cities in America: San Francisco, New York, and Portland. All three are victims of their own success, as rising demand for housing has increased rents to unsustainable levels. Despite their best efforts, from rent control to inclusionary zoning mandates, middle- and lower-class households are increasingly forced to leave these cities as each progressively transforms into a playground of the rich. Yet there is a fourth city, a city which must not be named except to be derided as a sprawling, suburban hellscape. This fourth city has managed to balance a booming economy, explosive population growth, and affordable housing. This city has—as cities have for thousands of years—steadily grown denser, more walkable, and more attractive to low-income migrants seeking opportunity. This city is Houston, and it’s well past time for her to come out of the shadows. Explosive Economic Growth, Booming Population, Functioning Housing Market Before jumping into the nitty-gritty of how Houston has handled explosive growth in the demand for housing, it is worth first getting a handle on the magnitude of the challenge facing the city. When many people think of the Houston economy, they understandably think of large energy companies. Indeed, energy companies dominated Houston’s economy for much of the last century and continue to play a major role today. But in the years following the 1980s oil glut, Houston’s economy has been diversified in large part by startups and emerging small […]
1. This week at Market Urbanism: Emily Washington champions Market Urbanist ideas on The Federalist radio hour Tory Gattis contributed How Houston Can Grow Gracefully: Snow White And The Nine Dwarves Each of these “villages” could comfortably grow to as much as a million people themselves, which, when added to 2-3 million in Houston, gets us as high as 12 million people in the metro area. Adam Hengels wants to loosen up on exclusionary zoning before trying other schemes: Exclusionary Zoning and “Inclusionary Zoning” Don’t Mix Given that, by definition, zoning is exclusionary, Inclusionary Zoning completely within the exclusionary paradigm is synonymous with Inclusionary Exclusion. Anthony Ling contributed an article translated from Portugueses: Densifying Transit Corridors Is Not Densifying Enough Many factors justify TODs’ attractiveness to current planners, including that they make transit viable, increase the centrally-located housing stock, and satisfy residents of low-rise areas, who usually enjoy keeping their neighborhoods’ original features. Zach Caceres made sense of the philosophy of the late Zaha Hadid‘s partner: The Bottom-Up Urbanism Of Patrik Schumacher Markets and open exchange are a ‘robust information processing system’—the best that humans have yet found. Cities are also ultimately about structuring information. The built environment embodies generations of lessons learned by humanity, the evolution of a community reflected in its roads and walls, and the deliberate structuring of human affairs through architecture. Michael Lewyn found evidence that not many real people object to home sharing such as AirBnb: To Know Home-Sharing Is To Support It Only 4 percent of Americans think home-sharing should be illegal, and only 30 percent think it should be taxed. 52 percent think homesharing should be legal and untaxed. Even among self-described liberals, only 38 percent think homesharing should be taxed. 2. Where’s Scott? Scott Beyer spent his 5th week in San Antonio. This weekend he’s visiting the Mexican border town of Nuevo Laredo, and the famed old […]

1. This week at Market Urbanism: Brent Gaisford contributed his first article, High Rent Sucks. Let’s Build More Houses and launched a new website: LA Rent Is Too Damned High Let’s upzone our cities and build more houses. And not just a few. A lot. Let’s build a lot more houses. Jeff Fong wrote a post inspired by a recent Nolan Gray piece, Planning As A Question Of Scale In Jane Jacob’s Hayekian Critique of Urban Planning, Nolan Gray argues for the futility of trying to master plan something as complex as an entire city. And he’s right. The last century’s Corbusian fantasies overwhelmingly ended in failure. Johnny Sanphillipo filmed a video about his small farm: Suburban Market Gardening This sort of small scale local food production is generally ignored or labelled as irrelevant. It isn’t “agriculture.” It isn’t…. anything. It’s just eccentric hobbyists who like to play farmer. But I disagree. Michael Lewyn is skeptical rich foreigners are causing high housing costs: Are Billionaires To Blame? One common argument I have read in various places is that the high rent of New York and other large cities is a result of globalization and inequality (English translation: rich foreigners). According to this theory, rich people have created a surge of demand so overwhelming that no amount of construction could possibly meet it. 2. Where’s Scott? Scott Beyer spent his fourth week in San Antonio. His Forbes article this week covered Puerto Rico’s business climate problem, focusing on the capital city of San Juan: Ricardo and Pamela were skeptical that one-stop permit shops would work in San Juan. The city would be too incompetent, settling for outdated technologies and low-energy employees. And special interests–such as existing businesses, entrenched civil servants and the gestores–would oppose streamlining the process. 3. At the Market Urbanism Facebook Group: via Logan Mohtashami: Build more houses […]
Adam Smith taught the world that mercantilism impoverished 18th-century nations by erecting barriers to trade and reducing opportunities for specialization and economic growth. Regulations that restrict urban development likewise reduce opportunities for innovation and specialization by limiting cities’ population size and density. Even as improvements in communications technology and falling transportation costs reduce the burden of distance, many industries still benefit from the geographical proximity of human beings that only dense development can provide. Removing land-use regulations will allow greater gains from trade as more people are allowed to live in important economic centers like New York City and Silicon Valley. Cities facilitate innovation by placing people with diverse backgrounds and goals in close proximity. While Israel Kirzner’s research provided a comprehensive analysis of entrepreneurs in the market process and in economic growth, economists have not given sufficient attention to the geography of entrepreneurship. The settings in which entrepreneurs work – Sandy Ikeda’s “action space” – matters, and cities provide a crucial role as the action space for much of human innovation. Silicon Valley is an urban action space where geographical proximity has made entrepreneurs more successful than they would have been without the inspiration they provided one another. The Homebrew Computer Club, a social group founded in 1975 for computer hobbyists, played a crucial role in the development of personal computers. The programmers, engineers, and inventors who attended those early meetings would go on to revolutionize computing thanks, in large part, to the information they gathered from swapping ideas, hardware, and skills from the other group members they encountered. The club began meeting in garages, parking lots, and university auditoriums, but it was only possible because these enthusiasts all worked for semiconductor companies that brought them to the same region of California. Empirical evidence bears out the importance of cities in facilitating […]

1. This week at Market Urbanism: Nolan Gray Reclaiming “Redneck” Urbanism: What Urban Planners Can Learn From Trailer Parks Trailer parks remain one of the last forms of housing in US cities provided by the market explicitly for low-income residents. Better still, they offer a working example of traditional urban design elements and private governance. Scott Beyer San Francisco Seeks Public, Not Private, Solutions To Housing Crisis However the biggest problem with San Francisco’s housing policy is that officials and citizens alike are hostile to new buildings, especially tall ones, even when they are built in appropriate locations. Emily Washington and Michael Hamilton Market Urbanism Is Underrated Zoning is not a Georgist tax in which landowners are taxed in proportion to their land’s value; rather, zoning hugely decreases the value of the country’s most valuable land, while it props up the value of land that would be less desirable absent zoning. 2. Where’s Scott? Scott flew early this week from his hometown of Charlottesville, VA to San Antonio. He has been hired by the Center for Opportunity Urbanism to do a profile on the city, including its history, growth, and future prospects. 3. At the Market Urbanism Facebook Group: Todd Litman, of the Victoria Transport Policy Institute, talks about The Disconnect Between Liberal Aspirations and Liberal Housing Policy John Morris says, “Ironic: Portland’s best shot at an equitable, environmentally sound, affordable city is to return to development before “progressive” planning.” Jeff Fong found interesting simulations predicting the promising effect of driverless cars on cities Lot’s of discussion about Tyler Cowen‘s skepticism that the deregulation Market Urbanism advocates won’t actually lower rents. (via Anthony Ling) Alex Tabarrok shared his latest post at Marginal Revolution: Regulatory Arbitrage, Rent-Seeking and the Deal of the Year where 4,000sf of valuable New York real estate had to be destroyed to comply with zoning “An eclectic coalition of residents, business owners, […]

Given that “redneck” and “hillbilly” remain the last acceptable stereotypes among polite society, it isn’t surprising that the stereotypical urban home of poor, recently rural whites remains an object of scorn. The mere mention of a trailer park conjures images of criminals in wifebeaters, moldy mattresses thrown awry, and Confederate flags. As with most social phenomena, there is a much more interesting reality behind this crass cliché. Trailer parks remain one of the last forms of housing in US cities provided by the market explicitly for low-income residents. Better still, they offer a working example of traditional urban design elements and private governance. Any discussion of trailer parks should start with the fact that most forms of low-income housing have been criminalized in nearly every major US city. Beginning in the 1920s, urban policymakers and planners started banning what they deemed as low-quality housing, including boarding houses, residential hotels, and low-quality apartments. Meanwhile, on the outer edges of many cities, urban policymakers undertook a policy of “mass eviction and demolition” of low-quality housing. Policymakers established bans on suburban shantytowns and self-built housing. In knocking out the bottom rung of urbanization, this ended the natural “filtering up” of cities as they expanded outward, replaced as we now know by static subdivisions of middle-class, single-family houses. The Housing Act of 1937 formalized this war on “slums” at the federal level and by the 1960s much of the emergent low-income urbanism in and around many U.S. cities was eliminated. In light of the United States’ century-long war on low-income housing, it’s something of a miracle that trailer parks survive. With an aftermarket trailer, trailer payments and park rent combined average around the remarkably low rents of $300 to $500. Even the typical new manufactured home, with combined trailer payments and park rent, costs […]
Several cities have jumped on the bandwagon of building Micro-apartments, a hot trend in apartment development. San Francisco and Seattle already have them. New York outlawed them, but is testing them on one project, and may legalize them again. Even developers in smaller cities like Denver and Grand Rapids are taking a shot at micro-apartments. At the same time, Chicago is building lots of apartments, and is known for having low barriers to entry for downtown development. Yet we aren’t hearing of much new construction of micro-apartments here. Premier studios are fetching as much as $2,000 a month. Certainly there must be demand for something more approachable to young professionals. In theory, we should expect to see Chicago leading the way in innovative small spaces. Chicago doesn’t have an outright ban on small apartments like New York, but there are four regulatory obstacles in the Chicago zoning code. These are outdated remnants from eras where excluding undesirable people were main objectives of zoning, and combined to effectively prohibit small apartments: 1. Minimum Average Size: Interestingly, there is no explicit prohibition of small units. This is unlike New York City’s zoning, which prohibits units smaller than 400sf. There is, however, a stipulation that the average gross size of apartments constructed within a development be greater that 500sf. Assuming 15% of your floor-plate is taken by hallways, lobbies, stairs, etc; this means for every 300sf unit, you need one 550sf unit to balance it out. Source: 17-2-0312 for residential; 17-4-0408 for downtown 2. Limits on “Efficiency Units”: Zoning stipulates a minimum percentage of “efficiency units” within a development. The highest density areas downtown allow as much as 50%, but these are the most expensive areas where land is most expensive. In areas traditionally more affordable, the ratio is as low as 20% to discourage studios, and encourage […]