Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Is it even possible today to write a vigorous argument in favor of the urban renewal policies of the 1950s? I doubt it. Jeanne Lowe's 1967 "Cities in a Race with Time* is a sympathetic account of the urban renewal era in its own terms. How does it hold up?
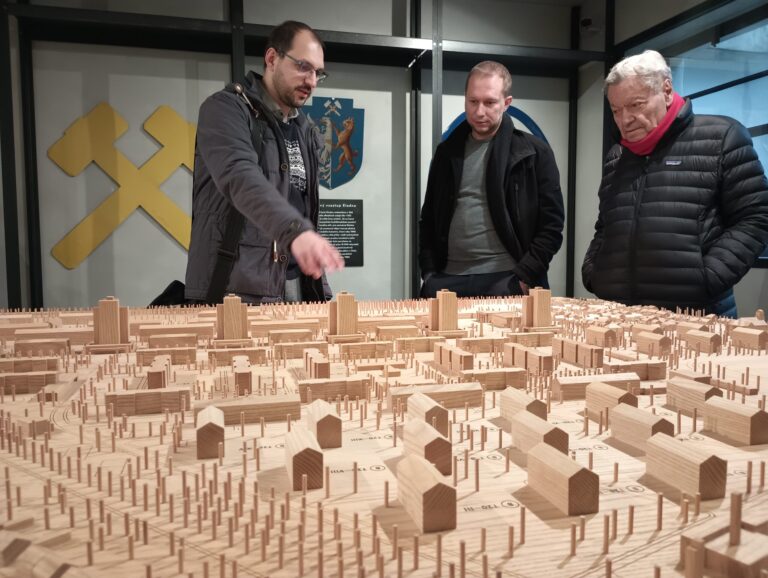

Most master plans are a costly effort by a team of temporary consultants, spread over two to three years, to prepare a blueprint that is usually obsolete as soon as it is completed.

Arbitrary Lines is the newest must read book on zoning by land use scholar and Market Urbanism contributor, Nolan Gray. The book is split into three sections, starting with what zoning is and where it comes from followed by chapters on its varied negative effects, and ending with recommendations for reform. For even deep in the weeds YIMBYs, it’s well worth picking up. There’s nothing dramatically controversial here, but give it a thorough read and you’re guaranteed to learn something new. In particular, the book’s third section on reforms is outstanding. It starts with a slate of policy proposals typical to this kind of text, but quickly goes much farther afield. After suggested policy changes, we’re invited to consider a world without zoning via an in-depth look at Houston’s land use regime. Here we’re treated to both an explanation of how it works and the unique political history that left the city unsaddled with zoning. Nolan goes on to close his recommendations with a call to reimagine what a city planner could be in a post-zoning American city; a call that, as a former New York City planner, he is uniquely fit to make. Aside from the content, this book deserves points for prose. Arbitrary Lines is blessedly readable. The writing flows and the varied anecdotes interspersed throughout the book make it feel less like a policy tract and more like a conversation with your favorite professor during office hours. For those already initiated, buy the book and enjoy nodding your head and learning a couple new things. And for those trying to share the good news of land use reform, consider making Arbitrary Lines that one thing you get friends or family to read. It’s among the most accessible books on land use I’ve ever read, and it’s a […]

Hayek says that planning is the road to serfdom. Holland may be the most thoroughly planned country on earth - and it's delightful. How does a market urbanist respond to excellent planning?

With Spider-Man: Far From Home hitting theaters earlier this month, the Marvel Cinematic Universe has taken one of the series’ biggest risks yet: pulling Spider-Man out of New York City. The gravity of this decision is baked into the film’s title — with good reason. More than any other Marvel superhero, Spider-Man is a uniquely urban superhero. Of course, his iconic powers — web-slinging and wall-crawling — depend on a forest of skyscrapers. But on a deeper level, Parker’s problems are quintessentially urban. Repeatedly, Peter encounters the issue of housing affordability, a recurring challenge for him and Aunt May in the comics and a key issue in the Sam Rami films from 2002 to 2007. In the Rami trilogy, Uncle Ben’s death pushes the family’s already-precarious financial situation into a monetary melee. We witness Aunt May desperately attempt to refinance, though she ultimately faces foreclosure and eviction. Rami’s Spider-Man (2002) stays true to the comics in putting Peter Parker’s family in Forest Hills — a well-heeled Queens neighborhood, depicted in the films as lower-middle class. Their home was assessed this year at approximately $850,000, which would entail a monthly mortgage payment of roughly $3,700 after a hefty downpayment. To make this affordable, Uncle Ben and Aunt May need to somehow make $135,000, a year before property taxes and upkeep. If that’s a stretch for a professional electrician, it’s impossible for a retired homemaker. The frustrations surrounding Aunt May’s eviction are an important part of Parker’s decision to give up being Spider-Man in the second film, and it’s easy to see why: May’s options post-eviction aren’t pretty. Assuming a standard Social Security check and a payout from Uncle Ben’s death, Aunt May really only has about $1,000 to spend on rent. Rising rents will make it tough to find a decent […]
It’s an understatement to say that zoning is a dry subject. But in a new video for the Institute for Humane Studies, Josh Oldham and Professor Sanford Ikeda (a regular contributor to this blog) manage to breath new life into this subject, accessibly explaining how zoning has transformed America’s cities. From housing affordability to mobility to economic and racial segregation to the Jacobs-Moses battle, they hit all the key notes in this succinct new video. If you need a go-to explainer video for the curious new urbanists, this is the one. Enjoy!
Turn the lights down, and the volume up. It's time for some Market Urbanist media, courtesy of some future urbanist leaders who's ideas may one day liberate our cities from yesterday's authoritarian planners.
1. Donald Shoup makes up for last week with an interesting piece on how America’s tax structure biases employers towards providing parking for their employees, similar to how untaxed employer-provided healthcare shapes that industry. 2. Back in August Randal O’Toole asked for proof that minimum parking requirements force Walmart to build more parking than they otherwise would. I think this is a bit of a red herring, since obviously parking reform would have more of an impact in areas that are more urban than where Walmart typically locates, but lo and behold, here’s the proof, at least in the case of one store in Northeastern Connecticut. In this case it looks like the parking minimums are going to be reduced, but I question whether smaller companies without Wal-Mart’s clout and money could have demanded such changes. 3. A survey of urban planners, supposedly biased towards big cities, found that 60% feel that the free market would not provide an adequate amount of parking if developers were not given parking minimums, with only 1 in 10 believing that the market would provide too much parking. The author of the paper, called “Are suburban TODs over-parked?” (.pdf), and published in the Journal of Public Transportation, found that suburban TOD projects in the East Bay and Portland supplied too much parking for the amount of cars that were actually parked. The authors unfortunately don’t do a great job of linking the parking surplus directly to parking minimums, but they do provide some interesting empirical evidence for what Matt Yglesias called “parking feedback loops” and what the study’s authors term a “virtuous cycle” – the idea that parking itself is a barrier to walkability, and thus removing spaces will lessen the demand for parking, even if nobody was using the spots that were removed.
I’ve been swamped in my day job, but want to share the following: The blog, Agents of Urbanism recently gave praise to Market Urbanism. Thanks Matthew! Please check out Agents of Urbanism and Life Without Buildings, who followed up on Agent of Urbanism’s praise. I enjoy both blogs. Carl Close wrote How “Urban Renewal” Destroyed San Francisco’s Fillmore District for The Independent Institute’s blog, The Beacon. And finally, I came across some fantastic lectures at the Foundation for Economic Education, by Sandy Ikeda. I highly recommend listening to the MP3s during your free time this weekend. He discusses Jane Jacobs, urbanism, history, sprawl, economics, and most things of interest to readers of Market Urbanism: Urban Planning Private Cities