Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
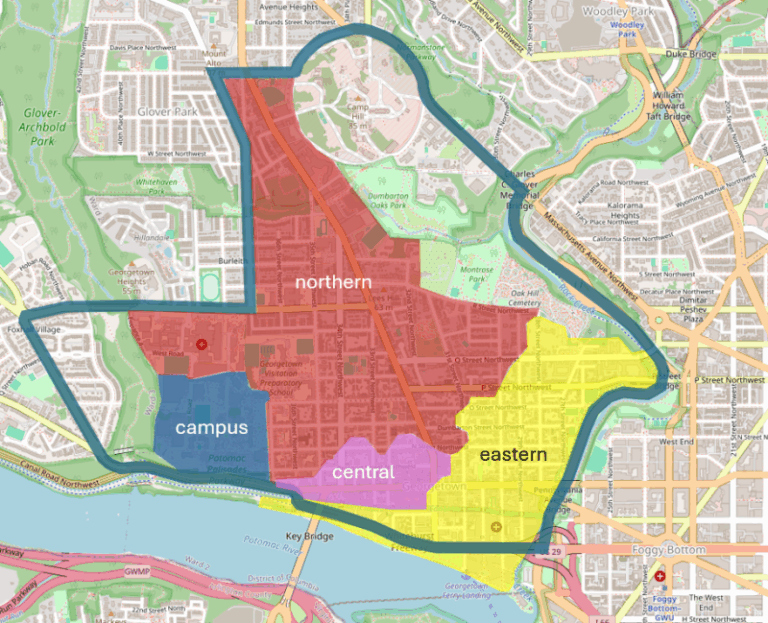
In Greater Greater Washington, my dad and I have a new editorial explaining how a ring-and-access traffic circulation plan inspired by the Netherlands can keep necessary traffic moving while delivering neighborhood streets and iconic shopping streets from traffic. Read the…
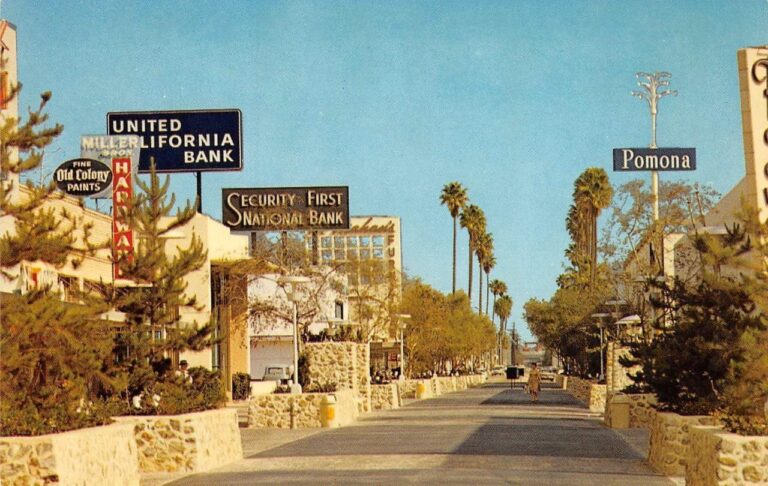

Urbanists love to celebrate, and replicate great urban spaces – and sometimes can’t understand why governments don’t: But what’s important to recall – especially for those of us under, uh, 41 – is that pedestrianized streets aren’t a new concept coming into style, they’re an old one that’s been in a three-decade decline. Samantha Matuke, Stephan Schmidt, and Wenzheng Li tracked the rise and decline of the pedestrian mall up to the onset of the pandemic. Even in the urbanizing 2000s and 2010s, 14 pedestrian malls were “demalled” against 4 streets that were pedestrianized: In a 1977 handbook promoting pedestrianization, Roberto Brambilla and Gianni Longo admit that some of the earliest “successes” had already failed: In Pomona, California, the first year [1962] the mall received nationwide press coverage as a successful model of urban revitalization; there was a 40 percent increase in sales. But the mall was slowly abandoned by its patrons, and now, after fifteen years of operation, it is almost totally deserted. A Handbook for Pedestrian Action, Roberto Brambilla and Gianni Longo, p. 25 One obvious reason for the failure of many other pedestrianized streets is that they were too little, too late. The pedestrian mall was one of several strategies against the overwhelming ebb tide of retail from downtowns in the postwar era. They weren’t seen as alternatives to driving, but destinations for drivers, who could park in the new, convenient downtown lots that replaced dangerous, defunct factories. A minority of the postwar-era malls survived. The predictors of survival are sort of obvious in hindsight: tourism, sunny weather, and lots of college students, among other things. Some of the streets which were “malled” and “demalled” have rebounded nicely in the 2000s. The slideshow below shows Sioux Falls’ Phillips Avenue in 1905, 1934, c. 1975, and 2015. The […]

Many readers of this blog know that government subsidizes driving- not just through road spending, but also through land use regulations that make walking and transit use inconvenient and dangerous. Gregory Shill, a professor at the University of Iowa College of Law, has written an excellent new paper that goes even further. Of course, Shill discusses anti-pedestrian regulations such as density limits and minimum parking requirements. But he also discusses government practices that make automobile use far more dangerous and polluting than it has to be. For example, environmental regulations focus on tailpipe emissions, but ignore environmental harm caused by roadbuilding and the automobile manufacturing process. Vehicle safety regulations make cars safer, but American crashworthiness regulations do not consider the safety of pedestrians in automobile/pedestrian crashes. Speeding laws allow very high speeds and are rarely enforced. If you don’t want to read the 100-page article, a more detailed discussion is at Streetsblog.

Last week DC Streetsblog reported on a new survey from Kaiser Permanente. The survey covers Americans’ attitudes toward walking and their self-reported walking habits. While a substantial majority of people believe that walking has health benefits ranging from weight management to alleviating depression, the survey found that most people walk less than the 150 minutes per week that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends. The Streetsblog coverage attributes a lack of walkable infrastructure to low walking rates, although it’s not clear to me that the survey explicitly supports this conclusion. However, past research demonstrates that people who live in neighborhoods where they are able to complete errands on foot do, unsurprisingly, do walk more than those who don’t. While people may not cite walkabilty as an important consideration in choosing a house, choosing a home involves weighing many factors, from size, price, distance to work and other amenities, aesthetic, and countless others factors. Consumers rely on tacit knowledge to weigh many of these factors because they can’t consciously enumerate all of them in making a decision of where to live. For this reason, revealed preference theory is a more reliable tool than survey data for observing how consumers value one attribute of a complex good like housing. Building on a past project, my colleague Eli Dourado and I are studying whether or not consumers do pay a premium for greater neighborhood walkability. Using a fixed-effects model, across all metropolitan and micropolitan statistical areas in the United States, our preliminary results indicate that, on average, Americans are willing to pay a premium of about $850 for a house with one additional point in Walk Score. Because of the many restrictions that limit walkable development, consumers have to pay this premium for the scarce supply of houses in walkable neighborhoods. This finding […]
photo at Brooklyn Paper was attributed to Montague Street Business Improvement District Stephen at rationalitate occasionally brings up that truly privatized streets could be converted to other uses. I think it would be inevitable that on streets with many shops and cafes, such as Montague Street in Brooklyn, the shops may get together to form some sort of association to own the street. Perhaps on weekdays, the association who own the street would allow commercial traffic which benefits their businesses, and on nights and weekends close off the street for seating and pedestrians. I guess we’ll never know until some city is bold enough to try it. Brooklyn Paper – Montague on grass! The grassy plazas would not cut off traffic on the busy side streets. As such, the bike advocacy group Transportation Alternatives said that the plan would not wreck havoc on car traffic. In fact, it would bring more people to the street, mostly by subway, foot or bike. “It will also encourage Sunday sales for our merchants,” said BID Executive Director Chelsea Mauldin. “People can come out, pick up a coffee, read the paper, and enjoy the sunshine.”