Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In many cities, poor people occupy valuable urban land close to downtown jobs, amenities, and transit. They can afford to live there because the housing stock in inner areas is usually older. If it hasn’t been completely renovated, the result can be quite cheap, even if the land is pretty valuable. In areas where there’s already some gentrification pressure, landlords face a timing problem: they can renovate (or sell to a developer) now, and cash out. Or they can hoard the property and wait until prices rise, supplying low-cost housing in the meantime. Land value taxes are specifically designed to penalize the hoard-and-wait approach by raising the annual tax cost of sitting on valuable land. It is specifically designed to accelerate neighborhood change. That’s the point. That’s what it says on the tin. Gentrification isn’t the only urban problem, and maybe it’s a small enough urban problem that a land value tax is a good idea anyway. But I think most of the benefits of Georgism can be unlocked with George-ish schemes (like renovation abatements or vacant land taxes) that are more narrowly designed.

In a recent Mackinac Policy conference, Detroit’s Mayor Mike Dugan proposed *drum roll* a land value tax. Sort of. Mayor Dugan’s proposal would create separate tax rates for land and capital improvements (i.e. the buildings on top). Specifically, he wants to decrease the tax rate on buildings by ~30% and increase rates on land by ~300%. The change would increase revenue for the city and also cause a series of second order effects. Taxing Blight & Rewarding Investment Detroit’s existing tax structure disincentives development. Holding vacant land or land with dilapidated (i.e. assessed as worthless) structures is cheap from a tax perspective. Actually developing land triggers a tax increase because of the brand new structure who’s value gets figured into the tax bill. What’s worse, the existing tax system encourages land hoarding. Land speculators sit on neglected parcels on the off chance that a developer needs it as part of a larger project. To caveat that, though, not all land speculation is bad. Holding some land off market and releasing it later into a development cycle can have positive benefits. In Detroit’s case, however, these are mostly vacant lots and abandoned buildings creating public health hazards the city has to deal with. The Political Economy of Land Value Taxation Unexpectedly – for me as a latte sipping coastal urbanite in California – Dugan’s LVT would also lower tax bills for homeowners. Land values in Detroit are low — in absolute terms and relative to structure values. Making the shift to taxing the less valuable land component of a property nets out positive for most homeowners. And the fact that it’s a win for homeowners makes me think it’s politically viable, both in Detroit and elsewhere. In places struggling to get back on a growth footing — places where land values […]
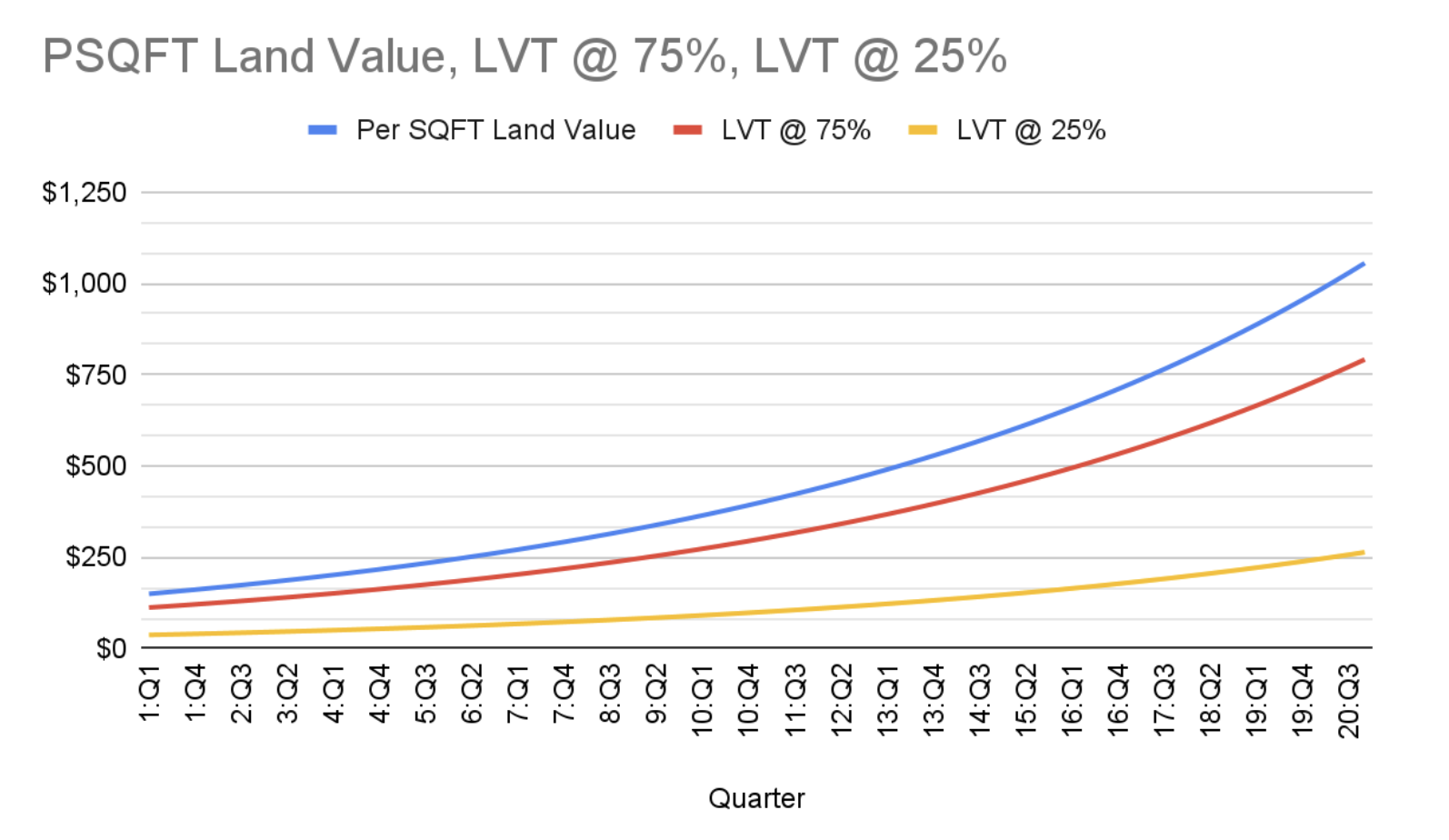
Georgists assert that a Land Value Tax (LVT) ensures land is always put to its most efficient use. They claim that increased carrying costs deter speculation. And if valuable land is never held out of use, society is better off. I think the story about incentives is correct. But I question whether pulling development forward in time is definitionally more efficient. In a world with transaction costs, tradeoffs abound and it’s worth thinking through the implications of an LVT. A Tale of Two Cities Picture a growing local economy with increasing land values and an LVT. Now suppose we split the time stream and create two parallel universes with different tax rates. In scenario A, we apply an LVT at 75%; in scenario B the LVT is set at 25%. There are two important questions here: 1) When will a given parcel be forced into development? 2) What intensity of development will the parcel support at the moment it’s put into productive use? To answer our first question, we look at the tax curves and make some assumptions. Suppose carrying costs push land into productive use at $250 psqft in LVT costs, scenario (a)’s parcel goes into development around year 9 at a $331 psqft. Scenario (b)’s parcel doesn’t see development until year 20 and a ~$1K psqft value. Given the delta between year 9 and year 20’s psqft valuations, we could expect to see different intensities of development. We’re now left with the question of whether a duplex in nine years is better than a mid-rise in twenty. Appropriating the full rental value of land would pull development forward, but that doesn’t definitionally lead to it being put to its highest and best use. Highest and best is contingent upon what time scale we’re optimizing for and that choice […]

Henry George and Jane Jacobs each have an enthusiastic following today, including, I’m sure, some readers of The Freeman. For those who might not know, Henry George is the late-19th-century American intellectual best known for his proposal of a “single tax” from which he believed the government could finance all its projects. He advocated eliminating all taxes except that on the rent of the unimproved portion of land. He viewed that rent as unjust and solely the result of general economic progress unrelated to the actions of landowners. Jane Jacobs, writing about one hundred years later, is an American intellectual best known for her harsh and incisive criticism of the heavy-handed urban planning of her day. She advised ambitious urban planners to first understand the microfoundations of urban processes — street life, social networks, entrepreneurship — before trying to impose their visions of an ideal city. Much has been written, pro and con, on George’s single tax and also on Jacobs’s battles with planners the likes of Robert Moses, and if you’re interested in those issues you can start with the links provided in this article. Here I would like to contrast their views on the nature of economic progress and the significance of cities in that progress. Some interesting parallels There are some interesting parallels between George and Jacobs. Both were public intellectuals who rebelled against mainstream economic thinking — for George it was classical economics, for Jacobs neoclassical economics. Both had a firm grasp of how markets work, were critical of crony capitalism, and concerned with the problems of “the common man.” And both established their reputations outside of academia. George was a strong advocate for free trade and an opponent of protectionism. He also understood Adam Smith’s explanation of the invisible hand. As George writes in […]