Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Conservative commentator Ben Shapiro has received some publicity for stating: “If you can’t afford to live here [in New York City] maybe you should not live here.” From the standpoint of advice to individuals,…
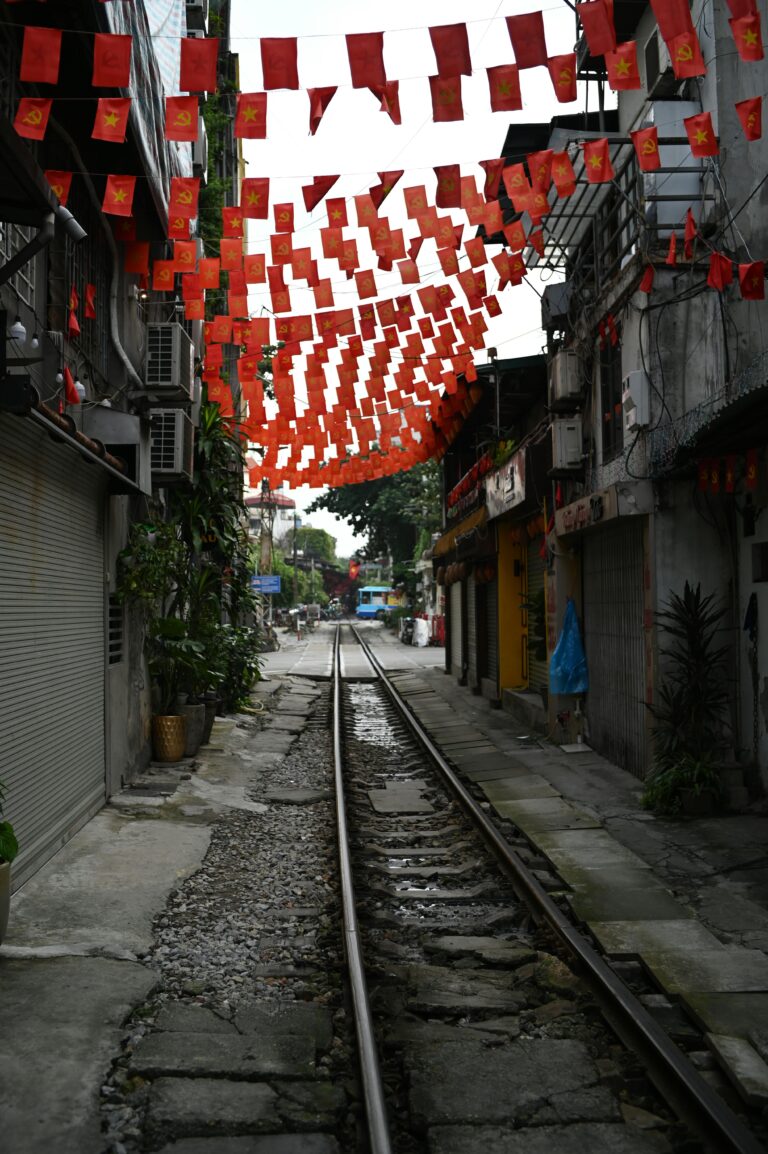

A Vietnamese business paper provides a fascinating window on land prices – official versus market – in an economy that has partially transitioned from socialism to markets: Hanoi has been collecting public feedback on…

Are rising prices in Kalamazoo a symptom of “climate refugees” moving to the cool, Rust Belt uplands? That’s a hypothesis put forward by a friend who works in the climate-insurance-housing cost nexus. It’s a…

I frequently reference my post summarizing the interesting research at last year’s Urban Economics Association conference. This year was as insight rich as ever. And the Montreal setting was truly special – it’s a…
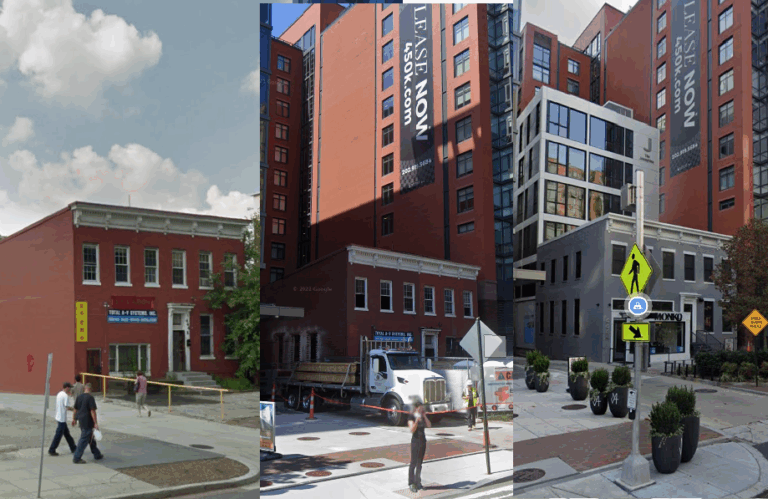

I walked down the 400 block of K St with an international guest last night. It was hard to describe the transformation of the street. Google Streetview, however, has been there almost since the…
In my day job, I suggested the name “Urbanity” for the research project that Emily Hamilton and I co-lead. I wasn’t sure about it myself, but it stuck. The noun urbanity, of course, refers…

On April 17, 1980, the Washington Post ran a curious paragraph, reporting a five-year-old quote for the first time – one withheld originally out of deference to the source: [Douglas Schneider’s] views of urban…
Sometimes, opponents of new housing claim that they aren’t really against all housing- they just want housing to be “gentle density” (which I think usually means “not tall”), or “affordable” (which I think usually…
Preservationists treat pre-1950 architecture as “historic” and irreplaceable, while often criticizing new building on a variety of aesthetic grounds. In his new book The Unfinished Metropolis, Benjamin Schneider points out that today’s historic buildings…
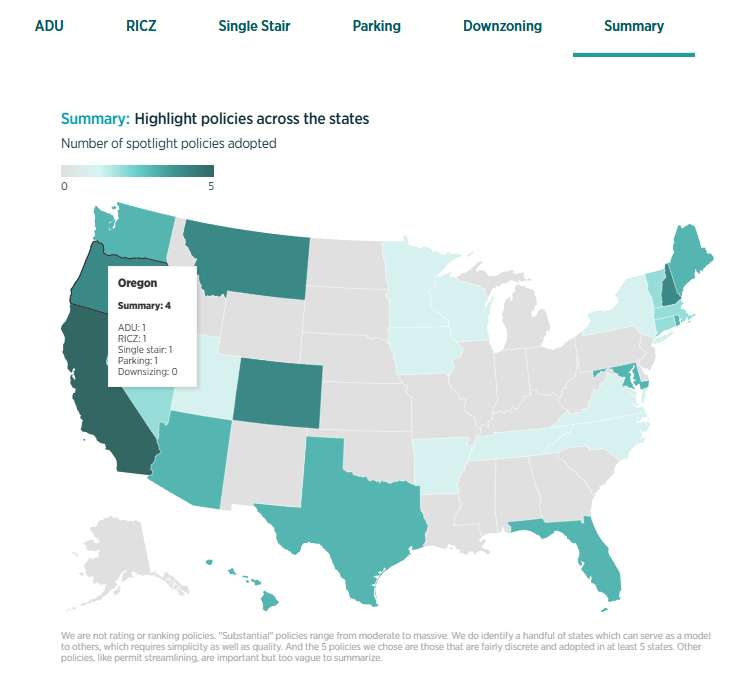
With a hugely productive legislative season in 2025, pro-homes legislators are rapidly taking good ideas around the country. To keep track of it all, my team created a new set of interactive maps. You…