Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
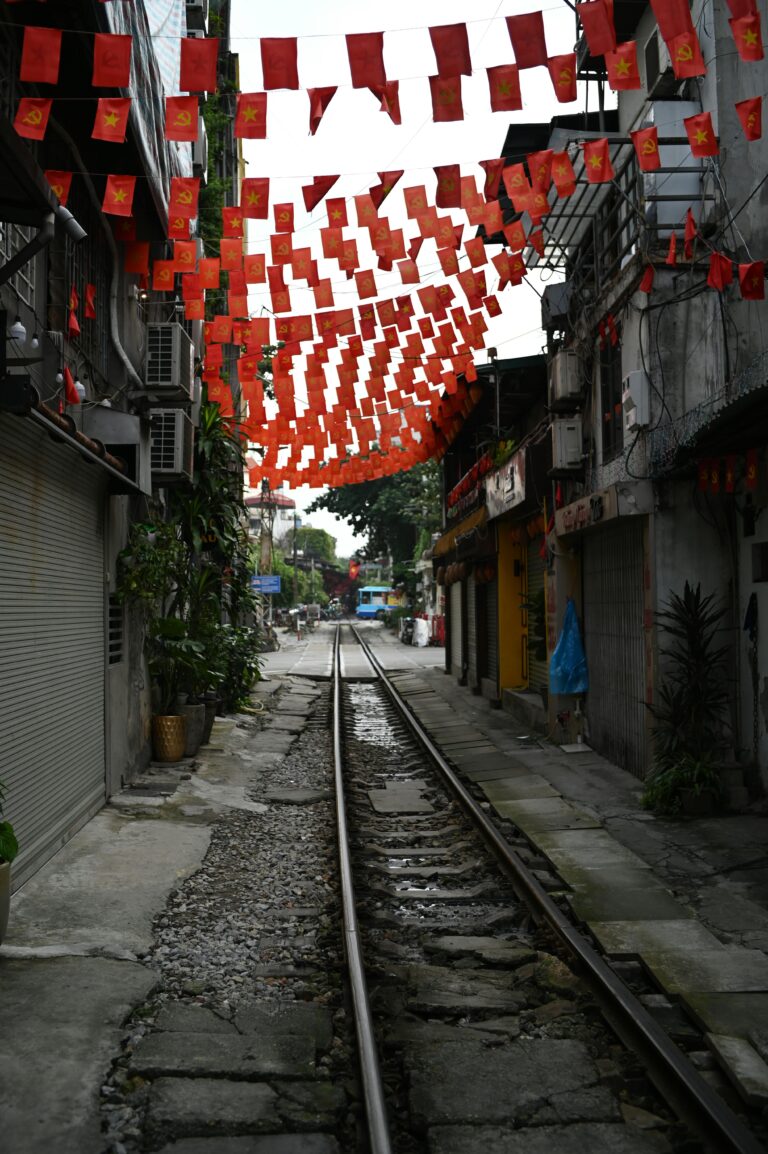

A Vietnamese business paper provides a fascinating window on land prices – official versus market – in an economy that has partially transitioned from socialism to markets: Hanoi has been collecting public feedback on its first-ever land price list, set…

Are rising prices in Kalamazoo a symptom of “climate refugees” moving to the cool, Rust Belt uplands? That’s a hypothesis put forward by a friend who works in the climate-insurance-housing cost nexus. It’s a provocative hypothesis. How else can one…
Three cool sites for data and visualizations
A common argument against new housing supply is that in high-cost cities such as New York, demand from foreign buyers is so overwhelming as to make new supply irrelevant. A recent study (available here) by two business school professors suggests otherwise. The study does show more foreign involvement in the NYC market than I expected: just over 13 percent of Manhattan buyers, and 5 percent of all regional buyers, come from outside metropolitan New York. Even this share is less than in some lower-cost markets: the study notes that 17 percent of Las Vegas buyers are from outside the city. However, the impact of “out of town” buyers is pretty small: the authors conclude that out-of-town buyers “cause an increase in house prices of 1.1% and an 39 increase in rents by 1.6% in both zones.”
One common argument against Airbnb and other home-sharing companies is that they reduce housing supply by taking housing units off the long-term market.* As I have written elsewhere, I don’t think home-sharing affects housing supply enough to matter. But even leaving aside the empirical question of whether this will always be true, there’s a theoretical problem with the argument that if someone fails to use their land for long-term rental housing, government must step in. It seems to me that this argument, if applied with even a minimal degree of consistency, leads to absurd results. For example, suppose that Grandma has a spare room in her house, and instead of renting it on Airbnb she allows the room to be unused. Should Grandma be forced to rent out the room? Of course not. A home-sharing critic might argue that an unused room is different from a room that is likely to be rented out to a long-term tenant. Indeed it is- but in fact, Grandma’s failure to rent the room to anyone is more socially harmful than her renting the room on Airbnb. In the latter situation, a traveler benefits (from a cheaper rate than a hotel, or at least for a different kind of experience) and Grandma benefits by getting money from the traveler. By contrast, in the former situation, no one benefits. It could be argued that Grandma’s rights should be unimpeded, but that regulation should be targeted towards the amateur hotelier who seeks to rent out an entire building all-year round, rather than using the building for more traditional tenants. Even here, the argument based on housing scarcity leads to absurd results. Suppose the evil landlord Snidely Whiplash decides, instead of renting out his building on Airbnb, to use the building for a vacation house one day a year […]