Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
One argument against Manhattan’s congestion pricing plan is that it merely redistributes congestion and pollution to nearby neighborhoods and suburbs, as drivers choose alternative routes that avoid midtown and downtown Manhattan. If this was true, air quality would decrease citywide…
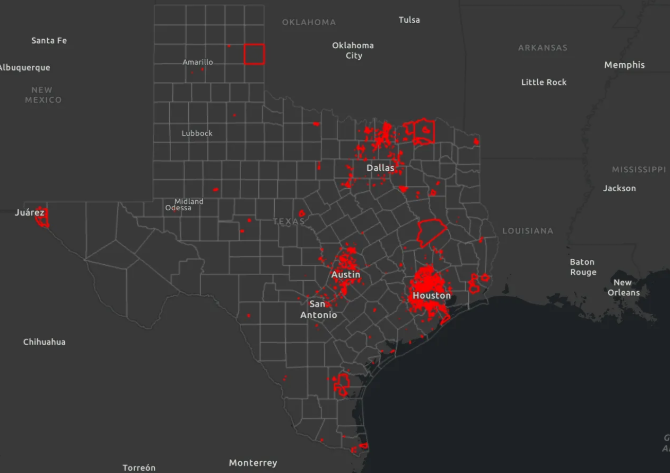
Connor Tabarrok has an excellent new primer on Texas Municipal Utility Districts (MUDs), covering history, function, governance, and critiques.

Because there are no market signals that could identify the best and highest use of street space, it is the role of urban planners to allocate the use of street space between different users and to design boundaries between them where needed.
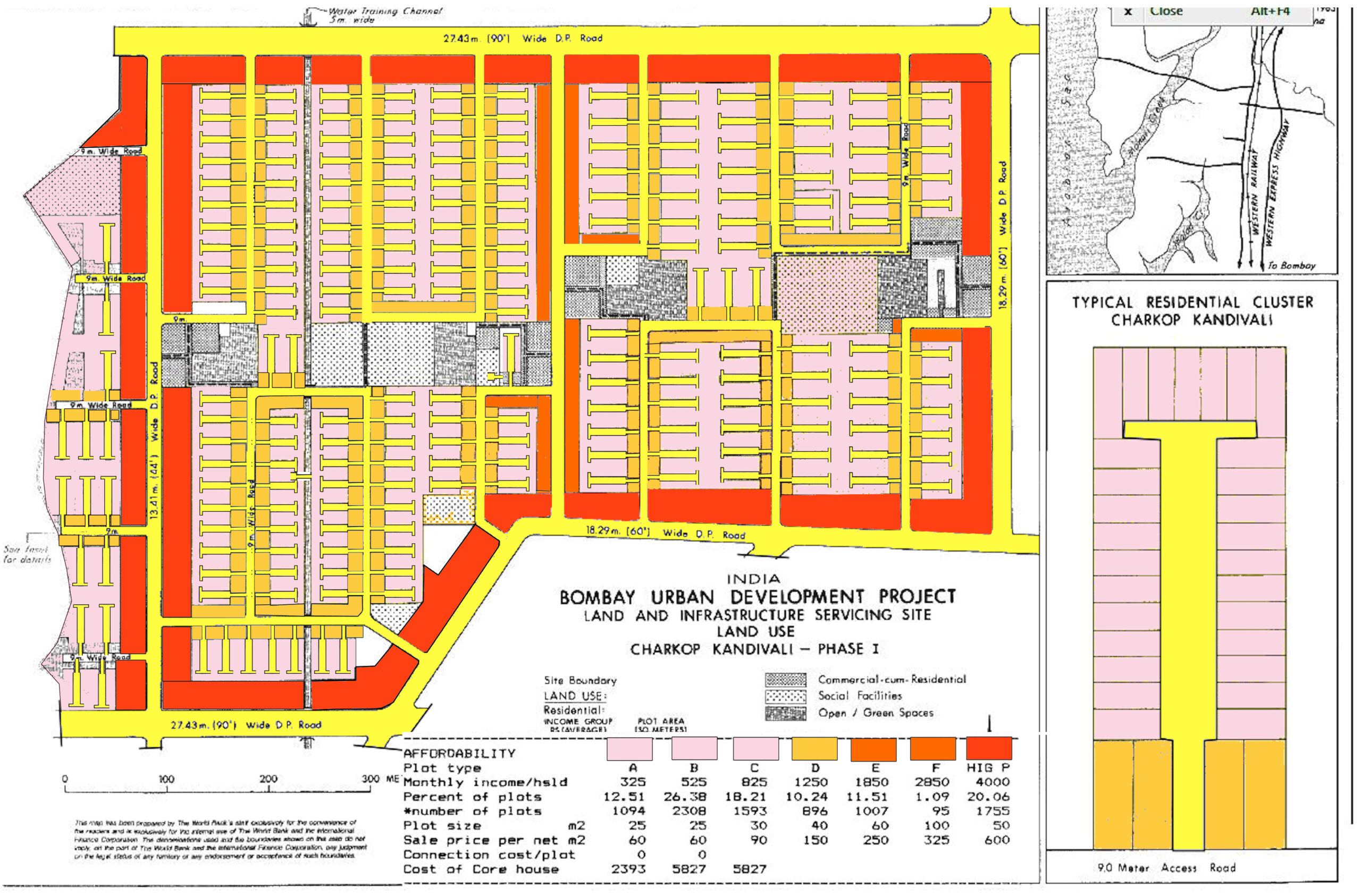
Alain Bertaud revisits a Mumbai development project he helped design in 1983. The neighborhood is thriving.
One argument against bus lanes, bicycle lanes, congestion pricing, elimination of minimum parking requirements, or indeed almost any transportation improvement that gets in the way of high-speed automobile traffic is that such changes to the status quo might make sense in the Upper West Side, but that outer borough residents need cars. This argument is based on the assumption that almost anyplace outside Manhattan or brownstone Brooklyn is roughly akin to a suburb where all but the poorest households own cars and drive them everywhere. If this was true, outer borough car ownership rates and car commuting rates would be roughly akin to the rest of the United States. But in fact, even at the outer edges of Queens and Brooklyn, a large minority of people don’t own cars, and a large majority of people do not use them regularly. For example, let’s take Forest Hills in central Queens, where I lived for my first two years in New York City. In Forest Hills, about 40 percent of households own no car. (By contrast, in Central Islip, the impoverished suburb Long Island where I teach, about 9 percent of households are car-free- a percentage similar to the national average). Moreover, most of the car owners in Forest Hills do not drive to work. According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey (ACS), only 28 percent of the neighborhood’s workers drive or carpool to work. Admittedly, Forest Hills is one of the more transit-oriented outer borough neighborhoods. What about the city’s so-called transit deserts, where workers rely solely on buses? One such neighborhood, a short ride from Forest Hills, is Kew Gardens Hills. In this middle-class, heavily Orthodox Jewish neighborhood, about 28 percent of households are car-free- not a majority, but again high by American or suburban standards. And even […]

With the Democrats scrambling to come up with a legislative agenda after their November takeover of the House of Representatives, an old idea is making a comeback: a “Green New Deal.” Once the flagship issue of the Green Party, an environmental stimulus package is now a cause de celebre among the Democratic Party’s progressive wing. While it looks like the party leadership isn’t too receptive to the idea, newly-elected Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez has spearheaded legislation designed to create a “Select Committee for a Green New Deal.” The mandate of the proposed committee is ambitious, possibly to a fault. At times utopian in flavor, the committee would pursue everything from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to labor law enforcement and universal health care. A recent plan from the progressive think tank Data for Progress is more disciplined, remaining focused on environmental issues, with clearer numerical targets for transitioning to renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Yet in all the talk about a Green New Deal, there’s a conspicuous omission that could fatally undermine efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions: little to no focus is placed on the way we plan urban land use. This is especially strange considering the outsized role that the way we live and travel plays in raising or lowering greenhouse gas emissions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), transportation and electricity account for more than half of the US’ greenhouse gas emissions. As David Owen points out in his book “Green Metropolis,” city dwellers drive less, consume less electricity, and throw out less trash than their rural and suburban peers. This means that if proponents of the Green New Deal are serious about reducing carbon emissions, they will have to help more people move to cities. One possible reason for this oversight is that urban planning […]
Some urbanists have become skeptical about the future of autonomous vehicles even as unstaffed, autonomous taxis are now serving customers in Phoenix and Japan. Others worry that AVs, if they are ever deployed widely, will make cities worse. Angie Schmitt posits that allowing AVs in cities without implementing deliberate pro-urban policies first will exacerbate the problems of cars in urban areas. However, cars themselves aren’t to blame for the problems they’ve caused in cities. Policymakers created rules that dedicated public space to cars and prioritized ease of driving over other important goals. Urbanists should be optimistic about the arrival of AVs because urbanist policy goals will be more politically tenable when humans are not behind the wheel. To avoid repeating mistakes of the past, policymakers should create rules that neither subsidize AVs nor give them carte blanche over government-owned rights-of-way. Multiple writers have pointed out that city policymakers should actively be designing policy for the driverless future, but few have spelled out concrete plans for successful driverless policy in cities. Here are three policies that urban policymakers should begin experimenting with right away in anticipation of AVs. Price Roadways Perhaps the biggest concern AVs present for urbanists is that they may increase demand for sprawl. AVs may drastically reduce highway commute times over a given distance through platooning, and if people find their trips in AVs to be time well-spent, when they can work, relax, or sleep, they may be willing to accept even more time-consuming commutes than they do today. As the burden of commuting decreases, they reason, people will travel farther to work. However, the looming increase in sprawl would be due in large part to subsidized roads, not AVs themselves. If riders would have to fully internalize the cost of using road space, they would think twice […]

On August 23rd, a California assembly bill aimed at increasing transit-oriented development, like housing, was passed by the state senate, confirmed by the assembly, and headed to Governor Jerry Brown’s desk for signing. The bill, AB 2923, specifically targets the San Francisco Bay Area—making it easier than ever for the Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) to build housing on the land it owns around its transit stations. Previously, housing developments on BART-owned land were still subject to local zoning rules, pushing projects through local processes to be approved before building began. This local control led to many delays, and, as a result, housing denials in the midst of an ongoing housing shortage—on that repeatedly spurs news headlines decrying four-plus hour super commutes, median home prices over $1 million, and neighborhoods blocking affordable housing. State bills like AB 2923 are a response to these reports, as well as the local control that led to them. If passed, AB 2923 and other bills like it, will bypass local control’s draconian rules to allow more housing to be built and ease the housing shortage. Under current law, land owned by BART is often subject to discretionary review in Bay Area cities. This forces BART to become de facto experts in every municipality zoning code, an impossible task that would take away from their focus on improving their transit system. Even attempting to master the zoning codes of every municipality takes time. Ultimately, this causes delays in building housing that’s so sorely needed. But this could easily be avoided if BART could establish their own zoning rules under AB 2923. Housing and transit is intrinsically linked and, just like suburban home developers build the roads to best suit their development, urban transit authorities like BART must utilize their capacity to build the homes best […]

On June 24 in Brooklyn, a driver in an SUV struck and killed four-year-old Luz Gonzalez, with many onlookers claiming the incident was a hit-and-run. The New York Police Department disagrees, and has refused to prosecute the driver, sparking multiple street protests. Beyond seeking justice for Gonzalez, activists demand that the city expand the use of speed cameras in school zones, which they hope could prevent further tragedy. Yet precisely at the moment that the community is most sensitive to the risk that dangerous driving poses to children, the New York state legislature shut off 140 school zone speed cameras. Given their unambiguous success in improving traffic safety in school zones, legislators should act now to renew and expand the program. While there is rare consensus among Governor Andrew Cuomo and Mayor Bill de Blasio on the need to preserve and even expand the traffic camera program to 290 cameras, the expansion faces opposition from some members in the Senate. Opposition to the cameras has been lead by Republican State Senator Martin J. Golden—himself a notorious school zone speeder, having received over 10 tickets since 2015 alone—and Democrat State Senator Simcha Felder, who ineffectively used the cameras as a bargaining chip to install police officers in schools. Since their implementation in 2014 as part of the broader Vision Zero initiative, school zone speed cameras have already substantially improved pedestrian safety in New York’s school zones. According to one study by the New York City Department of Transportation, the number of people killed or seriously injured in crashes in schools zones has fallen by 21 percent to 142 since the cameras came online. This is due in part to the fact that speeding drivers are getting the message: in the first 14 months following implementation of cameras, speeding violations in school […]
Suburb: Planning Politics and the Public Interest is a scholarly book about planning politics in Montgomery County, a (mostly) affluent suburb of Washington, D.C. The book contains chapters on redevelopment of inner ring, transit-friendly areas such as Friendship Heights and Silver Spring, but also discusses outer suburbs and the county’s agricultural areas. From my perspective, the most interesting section of the book was the chapter on Friendship Heights and Bethesda, two inner-ring areas near subway stops. When landowners proposed to redevelop these areas, the planning staff actually downzoned them (p. 56)- and NIMBYs fought the planning board, arguing that even more downzoning was necessary to prevent unwelcome development. These downzoning decisions were based on the staff’s “transportation capacity analysis”- the idea that an area’s roads can only support X feet of additional development. For example, Hanson writes that Friendship Heights “could support only 1.6 million square feet of additional development.” (p. 62). Similarly, he writes that Bethesda’s “roads and transit could handle only 12 million square feet of new development at an acceptable level of service.” (p. 75) Thus, planning staff artificially limited development based on “level of service “(LOS) . “Level of service” is a concept used to grade automobile traffic; where traffic is free-flowing the LOS is A. But the idea that development is inappropriate in low-LOS places seems a bit inconsistent with my experience. Bethesda and Friendship Heights zip codes have about 5000-10,000 people per square mile; many places with far more density seem to function adequately. For example, Kew Gardens Hills in central Queens has 27,000 people per square mile, relies on bus service, and yet seems to be a moderately popular area. Moreover, the use of LOS to cap density has a variety of other negative effects. First, places with free-flowing traffic tend to be dangerous for […]