Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Cities have always invited us to be constantly on the move. We move around to get to work, go shopping, meet friends, attend a concert, visit an art exhibition, and take advantage of all the many activities that a metropolis offers.
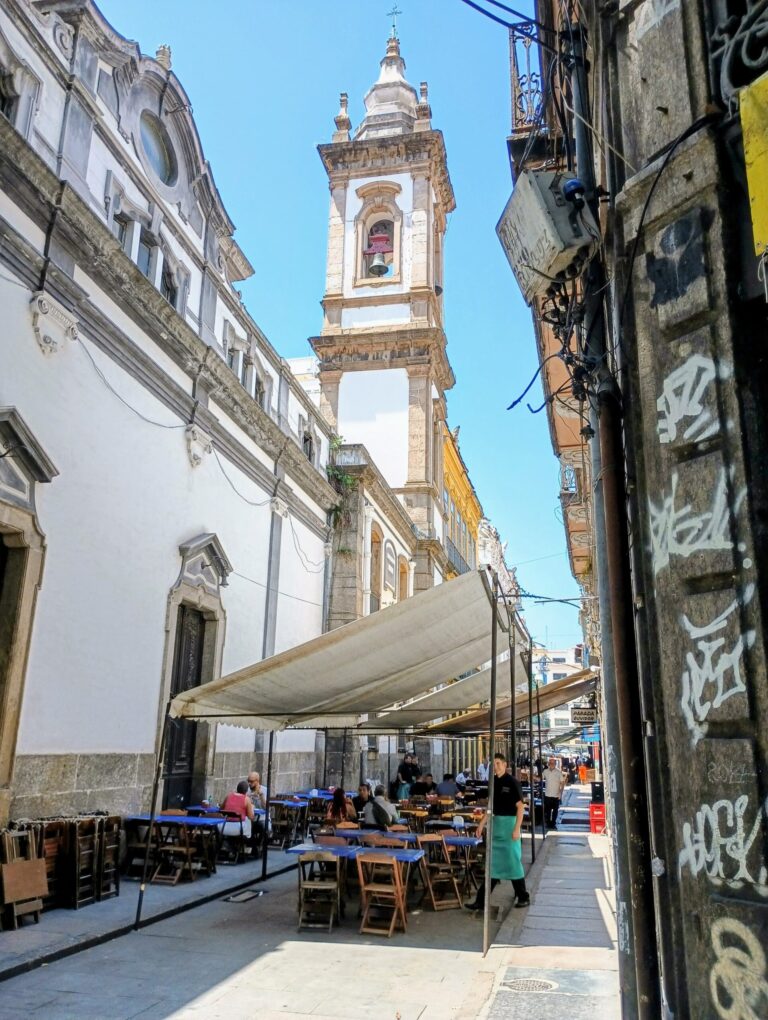
One common argument against mixing housing types and densities is that if housing type A (for example, townhouses or single-family homes) is mixed with housing type B (for example, condos), the neighborhood will somehow be “ruined” for residents of the less dense housing types. Last week, my new wife and I visited Chicago for our honeymoon. The most interesting street we visited, on Chicago’s wealthy Gold Coast, was Astor Street, just a block from high-rise dominated Lake Shore Drive. What is unusual about Astor Street is its mix of housing types. Although this street is dominated by large attached houses, it also has a few tall-ish buildings next to the townhouses, such as the 25-floor condo building at 1300 North Astor, the 20-story Astor Villas at 1430 North Astor, and the 27-story Park Astor condos at 1515 North Astor. Despite the tall buildings, this street felt like a quiet, beautiful, tree-shaded urban street. And the real estate market seems to agree: recent Zillow ads show a single-family house on Astor Street selling for over $2 million, and another one selling for over $3 million. By contrast, the average house in Astor Street’s zip code (60610) is valued at less than half a million dollars, and only 14.6 percent are worth over $1 million. Clearly, multifamily housing has not “ruined” Astor Street.
Lexington, Kentucky is a wonderful place, and that’s getting to be a problem. There’s nothing intrinsically wrong with the city: its urban amenities, thriving information economy, and unique local culture have brought in throngs of economic migrants from locales as exotic as Appalachia, Mexico, and the Rust Belt. The problem, rather, is that the city isn’t zoned to support this newfound attention. Over the past five years, the city has grown by an estimated 18,000 residents, putting Lexington’s population at approximately 314,488. Lexington has nearly tripled in size since 1970 and the trend shows no signs of stopping, with an estimated 100,000 new residents arriving by 2030. Despite this growth, new development has largely lagged behind: despite the boom in new residents, the city has only permitted the construction of 6,021 new housing units over the past five years—not an awful ratio when compared to a San Francisco, but still putting us firmly on the path toward shortages. The lion’s share of this new development has taken the form of new single-family houses on the periphery of town. Create your own infographics. Sources: ACS/Census Bureau At the risk of sounding like a broken record, there’s nothing intrinsically wrong with single-family housing on the periphery of town. Yet in the case of Lexington, it’s suspect as a sustainable source of affordable housing. Lexington was the first American city to adopt an urban growth boundary (UGB), a now popular land-use regulation that limits outward urban expansion. As originally conceived, the UGB program isn’t such a bad idea: the city would simultaneously preserve nearby farmland and natural areas (especially important for Lexington, given our idyllic surrounding countryside) while easing restrictions on infill development. Create your own infographics. Source: Census Bureau The trouble with Lexington is that the city has undertaken […]

A decade or two ago, a traveler who wished to stay in a city temporarily had no alternative to a hotel. Even if the owner of a house or condominium wished to rent out a room for a short period of time, the costs of advertising in a newspaper would have at least partially canceled out the financial benefits from renting. But the Internet has made home-sharing much more economical, through websites like Airbnb.com. At first glance, the home-sharing industry seems highly beneficial: guests get a cheaper and/or more exotic vacation, home-sharing hosts get extra money to pay off mortgages, and their neighborhoods benefit from tourist revenue. Nevertheless, NIMBYs have attacked home-sharing. One major argument is that home-sharing creates negative externalities. For example, a recent law review article(1) notes that some neighborhood activists in Silver Lake (a trendy Los Angeles neighborhood) sought to exclude home-sharing from their neighborhood on the ground that shared homes are “hotel-like room rentals” and such a “commercial use [causes] the noise and traffic levels of the area [to] increase as a result of people coming and going, and the transient nature of the establishment can increase the crime rate.” As a result of these problems, home-sharing “brings nuisances to residential areas, thereby lowering the value of all homes in the neighborhood.” In other words, the “externalities” argument rests on the following chain of logic: Assumption 1: Home-sharing, as a commercial use, is no different from hotels. Assumption 2: Commercial uses bring down property values. Conclusion: Home-sharing brings down property values. But none of these claims has significant factual support. First, home-sharing is somewhat different from a large hotel. An individual hotel might have hundreds or thousands of guests on one block. By contrast, home-shares tend to be spread out over a much larger space, […]