Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
“Renting in Providence puts city councilors in precarious situations.” That was the Providence Journal’s leading headline a few days ago, as the legislature waited for Governor Daniel McKee to sign a pile of housing-related bills (Update: He signed them all). Rhode Island doesn’t have a superstar city to garner headlines, but it’s housing costs have mounted as growth has crawled to a standstill. But unlike in Montana and Washington, Rhode Island’s were largely procedural, aiming to lubricate the the gears of its existing institutions rather than directly preempting local regulations. House Speaker Joseph Shekarchi (D-Warwick), who championed the reforms, clearly drew on his professional expertise as a zoning attorney to identify areas for procedural streamlining. Specific and objective Six bills transmitted to the governor cover the general rules affecting most Rhode Island zoning procedures: S 1032 makes it easier to acquire discretionary development permission. Municipalities cannot enforce regulations that make it near-impossible to build on legacy lots that do not meet current regulatory standards. Municipalities can more quickly issue variances and modifications. (Rhode Island draws a unique distinction between minor and substantial variances, labeling the former “modifications” and subjecting them to a simpler process. A substantial variance must go before a board for approval; a modification can be approved administratively unless a neighbor objects. Municipalities must issue “specific and objective” criteria for “special use permits”, otherwise those use are automatically allowed as of right. That phrase – specific and objective – shows up again and again in Speaker Shekarchi’s bills. S 1033 requires that zoning be updated to match a municipality’s own Comprehensive Plan within 18 months of a new plan’s adoption. It also requires an annually updated “strategic plan” for each municipality, although the content and legal force of the strategic plans are unclear to me. S 1034 broadly […]
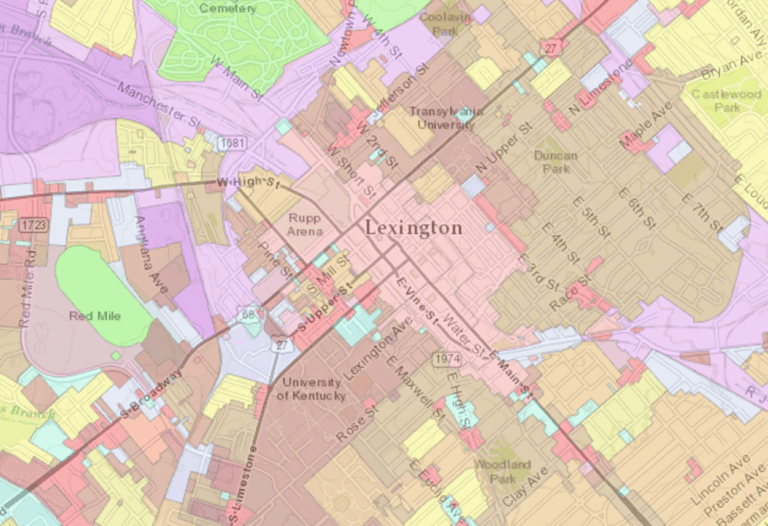
Lexington, Kentucky is a wonderful place, and that’s getting to be a problem. There’s nothing intrinsically wrong with the city: its urban amenities, thriving information economy, and unique local culture have brought in throngs of economic migrants from locales as exotic as Appalachia, Mexico, and the Rust Belt. The problem, rather, is that the city isn’t zoned to support this newfound attention. Over the past five years, the city has grown by an estimated 18,000 residents, putting Lexington’s population at approximately 314,488. Lexington has nearly tripled in size since 1970 and the trend shows no signs of stopping, with an estimated 100,000 new residents arriving by 2030. Despite this growth, new development has largely lagged behind: despite the boom in new residents, the city has only permitted the construction of 6,021 new housing units over the past five years—not an awful ratio when compared to a San Francisco, but still putting us firmly on the path toward shortages. The lion’s share of this new development has taken the form of new single-family houses on the periphery of town. Create your own infographics. Sources: ACS/Census Bureau At the risk of sounding like a broken record, there’s nothing intrinsically wrong with single-family housing on the periphery of town. Yet in the case of Lexington, it’s suspect as a sustainable source of affordable housing. Lexington was the first American city to adopt an urban growth boundary (UGB), a now popular land-use regulation that limits outward urban expansion. As originally conceived, the UGB program isn’t such a bad idea: the city would simultaneously preserve nearby farmland and natural areas (especially important for Lexington, given our idyllic surrounding countryside) while easing restrictions on infill development. Create your own infographics. Source: Census Bureau The trouble with Lexington is that the city has undertaken […]