Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In a recent post, I revealed the 91 large cities and counties that consistently fail to report complete data to the federal Building Permit Survey (BPS). But what about smaller jurisdictions, which often have weak record-keeping and slim staffs – and what about states made up of many such small jurisdictions?
The gold standard for counting housing units is the Decennial Census. That shows that the number of homes in Massachusetts grew from 2,622,000 in 2000 to 2,808,000 in 2010 to 2,998,000 in 2020. Even though building permits do not always result in completed homes, local reports and Census Bureau interpolations fall well short:
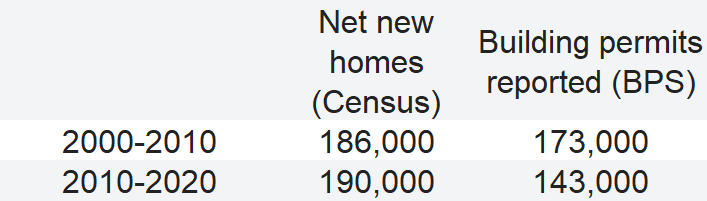
It’s possible that some building permits pulled in 2007-2009 were delayed by the Great Recession but completed after the 2010 census. Taking the twenty-year period together, the BPS (2000-2019) is only picking up 84 percent of completed homes – not to mention those that are permitted but abandoned.
Looking ahead, Gov. Healey’s administration has estimated (poorly) that the commonwealth needs 222,000 new homes by 2035. How does that compare to recent production? We don’t have a 2024 Census. But if we assume that reported 2015-2024 building permits turn into housing at the same rate that 2000-2019 building permits did, we can get a working estimate.
The BPS reports 167,000 Bay State building permits from 2015 through 2024 (with extrapolation for December, 2024). That means that something closer to 199,000 new homes were likely completed in that period. If that’s true, then the administration’s “housing need” estimate is just 12% higher than recent construction – which has been inadequate to prevent a huge upswing in rents and prices.